Generate a strong password with the random generator
The level of robustness corresponds to the size and complexity criteria selected.

Try LockSelf for 14 days
Generate strong passwords and store them encrypted in a French solution certified CSPN by ANSSI (Agence Nationale de la Sécurité des SI).
- Free of charge
- No credit card required
A random password generator for corporate security
Contents
Introduction
In an increasingly tense cyber environment, the strength of passwords is of paramount importance.
According to CESIN's 2023 report, phishing, which consists in recovering credentials, in particular passwords, remains the main vector of attack against companies.
Nearly 75% of all attacks start with phishing, because even a password, which at first glance has no impact on security, can lead to serious consequences if used skilfully by hackers. In this context, the use of a password safe is not only a practical solution, but also a security imperative.
Why are logins crucial to corporate security?
The way we work is changing, and the number of passwords is exploding.
With the strong digitalization of our organizations, which saw a second boom during COVID, the number of digital tools and applications enabling employees to manage, share or access information has risen sharply.
SaaS (software as a service) solutions, for example, have risen from 16 per employee in 2017 to over 130 in 2022! (Better Cloud study).
This multiplication of tools has mechanically increased the number of passwords to be managed by each person, leading to the emergence of well-known bad practices:
- Identical passwords for all applications.
- Passwords stored in web browsers.
- Passwords written in notebooks or on post-it notes.
- Passwords stored in a csv file on the desktop.
Indeed, for each of our tools, a unique password must be created, managed, stored and even renewed regularly to limit the risk of leaks.
Passwords: an essential business issue
Passwords are the gateway to a multitude of digital resources.
They secure access to crucial data such as :
- Employees' or customers' personal data (via CRM, for example)
- Access to internal company tools (e.g. Back-Office)
- Company social networks
- Customer accounts (for agencies)
- Access to IT department resources
- Financial or accounting statements (via treasury tools)
It's obvious, then, that entrusting the creation of these accesses to each employee can generate a considerable risk of cyber-attack.
Employees, for reasons of convenience, often tend to create simple, memorable passwords or use the same password everywhere, an open door for cyber attackers.
A project called Projet Richelieu has in fact been developed in 2019 to help those responsible for data security within companies to better protect access, the genesis of which is as follows:
"Richelieu" is a list of the most common French passwords. It is based on publicly known data leaks. These leaks have been reworked to retain only those passwords linked to email addresses ending in ".fr". In addition, the list obtained is frequently analyzed to find the most common passwords.
The aim is to provide French CISOs and CIOs with a more accurate dictionary for conducting security tests on their infrastructure via brute force attacks."

Maxime Alay-Eddine
Dictionary attacks are often used in cryptanalysis to test the robustness of accesses. They simply consist of testing all the passwords present in a "dictionary" (a list of commonly used identifiers) to verify that the access used is indeed unique and robust, and that its length is sufficient.
Weak passwords: an entry point for cyber-attacks.
Everyone has used "1234" as a password at least once.
You might think that weak passwords are only used for useless accounts, and that everyone uses more complex strings of characters, containing upper and lower case, numbers and even special characters, to make their online accounts as secure as possible.
However, the importance of protecting one's data has not yet taken root for everyone, and many people use simplistic identifiers or identifiers based on personal information such as their date of birth, which are therefore not very robust.
The statistics are alarming: a recent study by Verizon shows that a large majority of data breaches are due to weak or stolen passwords, illustrating the extent of the threat to corporate security posed by weak passwords.
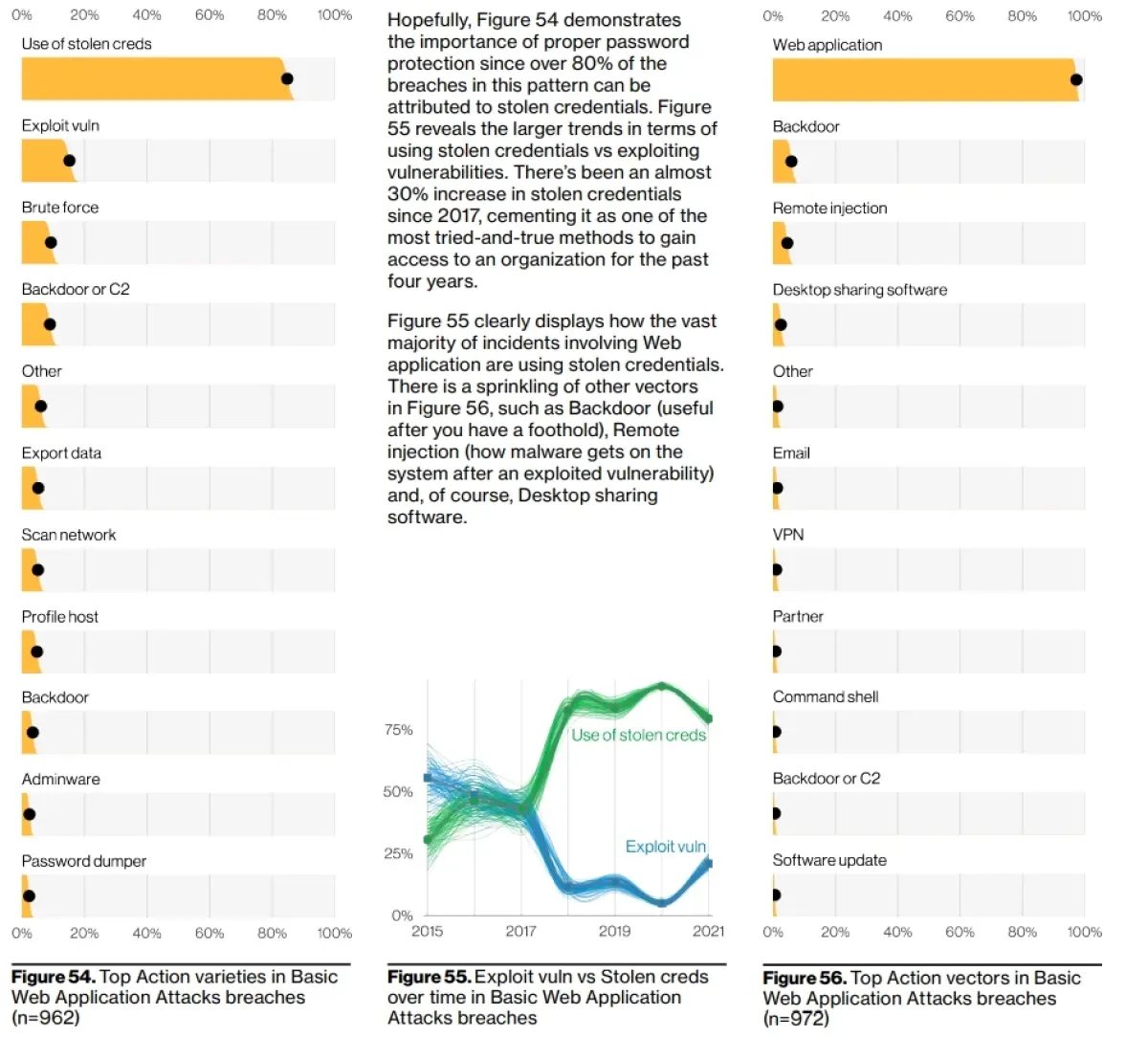
Verizon study - Data Breach 2022
The key is to banish bad practices on the part of employees, so that all your data is effectively protected, while at the same time establishing clear security methods and policies that can be easily applied by all staff.
Why use a random password generator?
The benefits of generating random passwords
Using a random password generator offers two guarantees: robustness and uniqueness.
- Robustness: you can be sure that your passwords will be strong and secure.
- Uniqueness: All your accesses will be generated in the same way, so none can represent a weakness.
A randomly generated password is almost impossible to guess, as it follows no logical or predictable pattern.
However, if the length of the identifier is insufficient, or if it uses only one type of character (only numbers or lower case letters), it may still be susceptible to a brute force attack, even though it is, on the face of it, robust.
But another challenge remains: the management and storage of these passwords.
Writing passwords down on a post-it note, an Excel file or on your phone is clearly not the solution, given the risk of loss or theft. Yet this is a behavior often observed by CISOs or cyber managers within companies.
Unfortunately, it can be difficult to change the password management habits of less technical staff. The latter are not opposed to the idea of adopting more secure practices, but it must remain quick and easy to use, so as not to hinder their productivity.
We'll see later how to manage your passwords, once they've been randomly generated.
Compliance with cybersecurity rules
Today, there are a number of standards governing passwords and password generation.
These guidelines give organizations a framework for securing their access.
Here are three of them:
- ANSSI recommendations;
- CNIL recommendations;
- The ISO27001 standard.
One of the most important points to bear in mind when choosing to generate random passwords is that you can more easily enforce ANSSI (Agence nationale de la sécurité des systèmes d'information) recommendations within your organization.
According to the ANSSI, a password must be at least 15 characters long, and contain a mix of upper and lower case letters, numbers and special characters to be considered strong.
Although these rules can be respected without the help of a generator, users tend to create predictable passwords, the better to remember them, by incorporating numbers and symbols transparently, for example by transforming "password" into "p@ssw0rd".
These a priori robust versions of passwords are well known to hackers and do not represent reliable security against them.
A random generator avoids these pitfalls by creating unpredictable, complex and therefore more secure combinations.
In addition to reducing the risk of cyber-attacks, the use of a password generator enables you to comply with CNIL guidelines.
Although the CNIL recommends the use of double authentication rather than a single password, it admits that a single secure password is sufficient for many uses, particularly those not involving personal data.
Finally, whether you are seeking to obtain or renew ISO 27001 certification, the latter also lays down a clear framework around the question of "Who has access to what?".
This question is an integral part of the standard, and should therefore also guide your thinking and work.
More specifically, appendix A.9 of the standard addresses the issue of logical access control through 4 subsections, which we have summarized below:
- A.9.1 Business requirements for access control: Define processes detailing who should have access to what.
- A.9.2 User access management: Define processes for managing employeeaccess to information over time (granting and revoking access rights).
- A.9.3 User responsibility: Define processes enabling employees to generate sufficiently robust access (password generator) and share it with the right people (centralized manager).
- A.9.4 Responsibility for access to systems and applications : Define access rights for everyone in the organization.
Strong passwords for your entire company
Using a random password generator on an individual basis is a first step towards reducing the risk of cyber-attacks, and should become a habit.
Ideally, however, it should become a habit for as many people in your teams as possible.
Several levers can be put in place, and should ideally be activated jointly:
- Make a random password generator available to all employees.
- Define one or more password policies and impose them according to the rights and privileges of each individual.
- Communicate best practices and tools.
This "communication" lever is essential to anchor the right reflexes in the daily lives of all employees:
- Use a random password generator to create and/or renew passwords.
- Generate passwords via the generator in compliance with the company's password policy.
- Use a centralized password manager to manage passwords on a daily basis and access the right resources directly.
Deploying a random password generator at every level of the company, with an appropriate password policy, ensures uniformity of password security.
This uniqueness is essential in cybersecurity because, let's not forget, even seemingly innocuous access can simplify the lateralization of an attacker within the company's information system and the recovery of critical information.A successful phishing attack on a member of a team can ultimately lead to an attack on a senior executive, enabling him or her to extort confidential data. This is known associal engineering fraud.
How do I use a random password generator?
What parameters should be used when generating a strong password?
"How do I create a secure password?" You've probably already asked yourself this question.
It's actually quite simple.
There are two main parameters influencing the strength of a password:
- The number of characters used - quite simply, the length of the password.
- The set from which these characters are drawn. By set, we mean all the characters that can be included in your password.
When creating a password, ANSSI recommendations suggest a minimum of 15 characters from a wide range of symbols, including uppercase, lowercase, numbers and special characters.
At LockSelf, we recommend going beyond this, opting for a length of 18 characters.
This recommendation, while seemingly more demanding, offers increased security at minimal cost in terms of complexity. And with the right tools, there's nothing to stop you from opting for much longer lengths, to always offer more robust access.
In fact, according to a study by Hive Systems, an 18-character password exponentially increases the time required for a potential hacker, thus considerably reinforcing the security barrier against hackers.
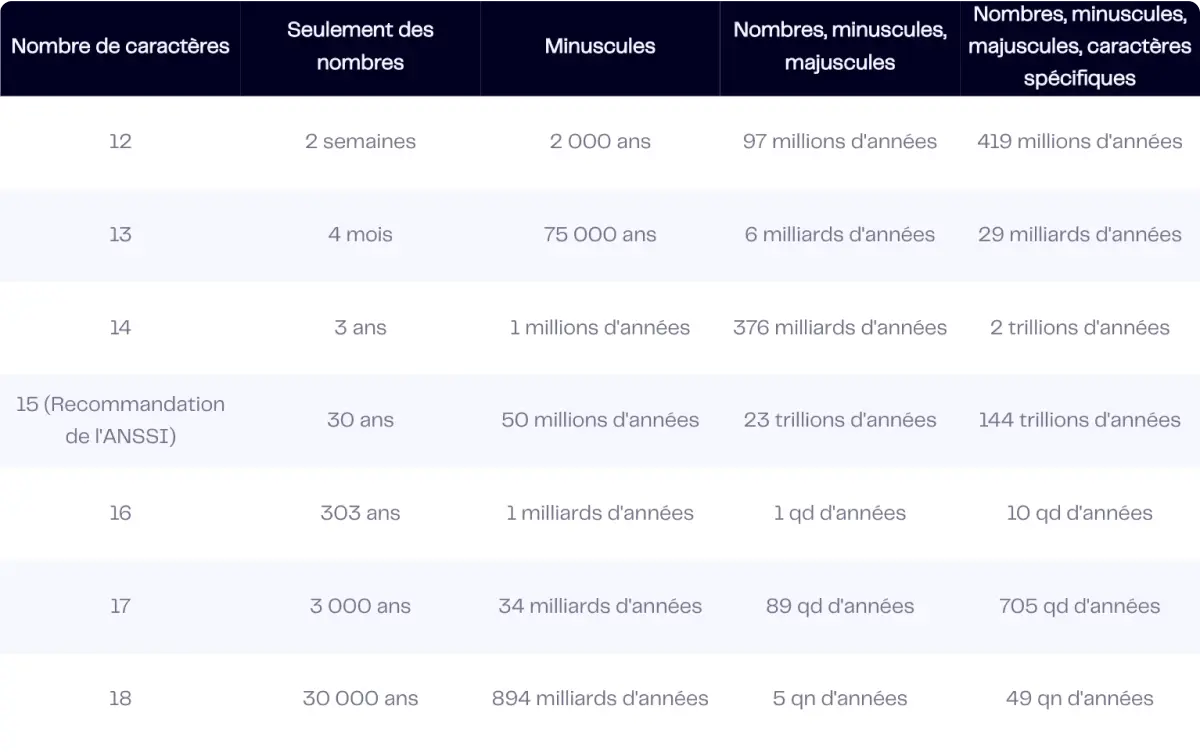
Password strength according to composition and ANSSI recommendations.
To conclude on the subject of best practices in random password generation, one existing method is the passphrase. Passphrases are an interesting alternative to traditional passwords, as they contain many more characters.
These sequences of words often form meaningful sentences, making them easier to memorize and relatively robust. However, passphrases are not without their flaws. Their generation is not always random, and they may lack diversity in terms of characters, thus limiting their effectiveness. For example, according to a study by hive système, simply combining numbers with lower-case letters can multiply the robustness of a password by a factor of 100 or more.
This is why passphrases often made up of letters only can be problematic.
What's more, if you don't use a tool to store your credentials, a passphrase may be difficult to remember, even if it makes sense.
How to combine the generator with other security measures.
It's imperative to remind your staff and management that, while strong passwords are essential, they are only one facet of the overall security strategy. Passwords can be stolen through phishing attacks, for example, in which case their strength is of little importance.
ANSSI therefore recommends the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to reinforce account protection. Combining strong, randomly generated passwords with other forms of authentication, such as telephone validation or security keys, forms a much stronger bulwark against intrusion attempts.
Storing passwords: an all-too-common mistake
As mentioned earlier in this article, one of the most common pitfalls in password management is inadequate storage.
"Having a lock that's difficult to force is a great start, but if the key is left in plain sight, efforts are in vain."
We often met CIOs worried about password issues because their employees were storing passwords on :
- Post-its left in plain sight
- excel files exchanged by drive
- Directly in instant messaging systems (e.g. Slack)
- In e-mails exchanged sometimes over several months
- In their phone on a note.
The combined use of password generators and password managers is therefore crucial.
The latter enable all passwords to be stored securely, eliminating the need to memorize them or write them down on vulnerable media.
And for even greater speed and simplicity, password managers offer tools for auto-filling fields via browser plugins, so you can log in with just two clicks, or record your new accesses when creating an account.
A very practical feature when you consider the number of passwords a single person has to manage every day.
Integrate Lockself's password generator into your information system
As we have already mentioned, you need a random password generator to make your access as secure as possible.
Then, to avoid any storage problems, you need to couple this generator with a password manager to keep passwords in a safe place.
Finally, with regard to access management, the answer to the question: "Who has access to what?" You also need to be careful to select a manager designed for businesses, which will facilitate your work as administrator and security manager.
If we sum up these three points, we get:
- Robust password generation forced by a suitable policy
- A secure safe to store every account in your company
- Advanced safe management to properly allocate and track access usage.
LockPass, LockSelf's password safe, meets all three of these requirements, and includes a password generator, an adapted version of which you can test on this page.
The ANSSI-certified password manager
Discover LockPass, the password manager for businesses. Strong passwords, guaranteed access traceability, 100% French and secure.
- Encryption
- Easy to use

Activate your free trial now!
With LockSelf, equip your teams with a suite of simple tools to manage their passwords and share their files in total security.
- Reduce your company's exposure to cyber attacks.
- Combating digital malpractice.
